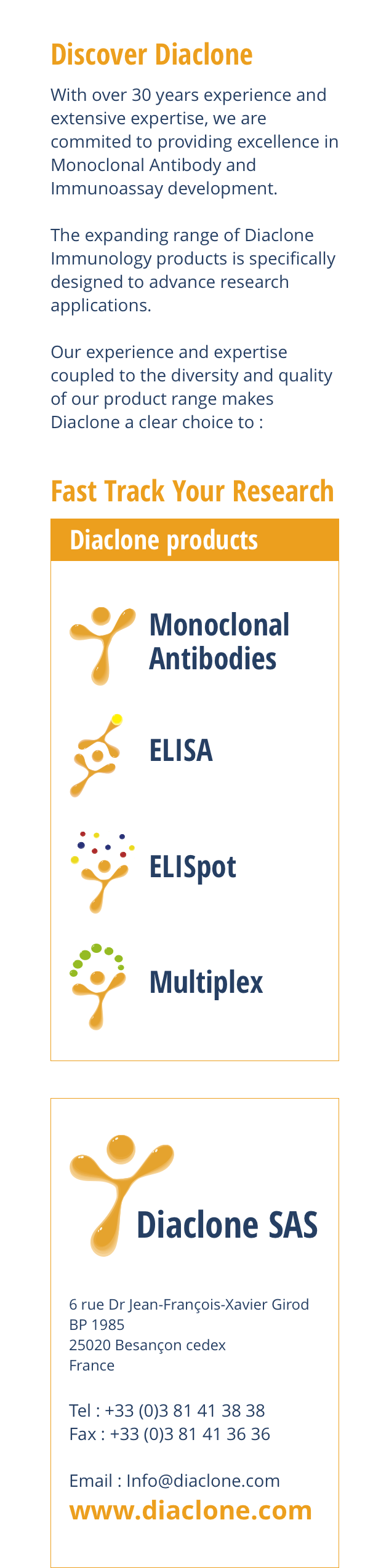
Anti-Human CD154 Azide Free
Product Specifications
- Catalogue N°
- 854.290.000 - 200µg / 200µl
854.290.005 - 500µg / 500µl - Target species
- Human
- Specificity
- Recognises the CD40L, TRAP, T-BAM antigen, a 28/30/33 kDa protein
- Clone
- B-B29
- Application
- Flow Cytometry
- Hybridoma
- Myeloma X63/AG.8653 x Balb/c spleen cells
- Immunisation
- CD40L transfected 3T6 cell line
- Quantity
- 200µg or 500µg (Discovery Size also available please enquire)
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2a Kappa light chain
- Format
- Phosphate-buffered saline. Sterile-filtered through 0.22 µm. Carrier and preservative free
- Storage
- Stable at +2-8°C for 12 months. For longer storage freeze aliquots.
- Synonym
- CD40 Ligand
- TRAP
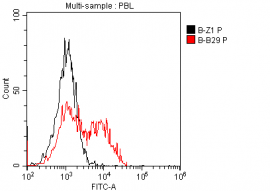
(background coloration by hematoxylin).
References
- Wassmer, S. C. et al.,J Infect Dis.,2004;189(2):180-9 - Pubmed link
- Yu, J. et al., Cancer Biother Radiopharm,2008; 23(3): 342-54. - Pubmed link
BACKGROUND
CD40 belongs to the TNF receptor superfamily. While the biological role of some of the ligand-receptor pairs in this family still remains obscure, CD40 has proven its importance.
A key role of CD40/CD40ligand interactions in immune activation, particularly in T-cell dependent B cell responses is anticipated. This molecule as well as the other ligands of the family share the property of co-stimulation of T-cell proliferation and are all expressed by activated T-cells.
The programmed cell death has been suggested to be involved in clonal elimination of self-reactive lymphocytes for the normal function of the immune system. Interaction with membrane bound self antigens may eliminate self-reactive nature B cells by apoptosis. Antigen-receptor mediated B cell apoptosis is blocked when a signal is transduced via the CD40 molecule on the B cell surface.
Because the ligand of CD40 (CD40L) is expressed on activated T helper cells, B cells may escape from apoptosis and are activated when the immune system interacts with foreign antigens, which are normally able to activate T-helper cells. Thus the CD40 - CD40L interaction plays a central role in the various phases of the B cell response to T-dependent antigens.
Taken together, B cells can participate in regulating their own destruction. Protection against Fas-dependent apoptosis afforded by immunoglobulin-receptor engagement may constitute a fail-safe mechanism that eliminates bystander B cells activated by CD40L - expressing T cells, but ensures survival of antigen-specific B cells.
CD40 Ligand is expressed on the surface of activated CD4+ T cells, basophils, and mast cells. Binding of CD40L to its receptor, CD40, on the surface of B cells stimulates B-cell proliferation, adhesion and differentiation. A soluble isoform of CD40L has been shown to exist in the circulation. This soluble molecule is a homotrimer of a 18kDa protein exhibiting full activity in B cell proliferation and differentiation assays, is able to rescue B cells from apoptosis and binds soluble CD40.
CD40L is discussed in relation to a potential role in supporting B cell tumors and it has been discovered that the molecular defect in the X-linked Hyper-IgM-Syndrome is targeted to the CD40L gene, it is functional involved in B cell hybridomas and chronic lymphocytic leukemia as well as several autoimmune diseases.
Version 10 - 04.21
For research use only
For any order, the purchaser acknowledges having read and accepted the terms and conditions described on the Diaclone website.