Phage Display
Diaclone phage display platform, an alternative approach to monoclonal antibody development
Phage display is a method that allows the selection of a peptide (antibody, protein, ...) through its presentation on the surface of phages. In short, a phage library expressing a wide diversity of peptides or proteins is used to select those binding the desired targets.
Phage display is a powerful technique and can be a good alternative to the conventional hybridoma method:
- Fast process (4 – 6 months)
- Better diversity
- Stability of clones
- Possibility to obtain recombinations not present in the natural form
- Available formats: Fab, ScFv, VHH, Full recombinant antibody
- Different species: mouse, rabbit, llama, amongst others…
Diaclone is specialized in advanced monoclonal antibody development technologies for a wide range of service projects. To complete our hybridoma platform, we can now offer high-quality mouse phage display library construction and custom phage display library screening services to precisely meet your needs.
Our phage display technicity allows the development of mAbs particularly difficult to obtain with a classical fusion and offers you new opportunities in several applications in R&D, diagnosis and immunotherapy: antibody for cytometry, IHC, Western blot…applications, neutralizing antibody for immunotherapy, ScFv for CAR-T program, amongst others.
Discover: Diaclone, your full-service antibody manufacturing and engineering partner
Standard Phage Display Project
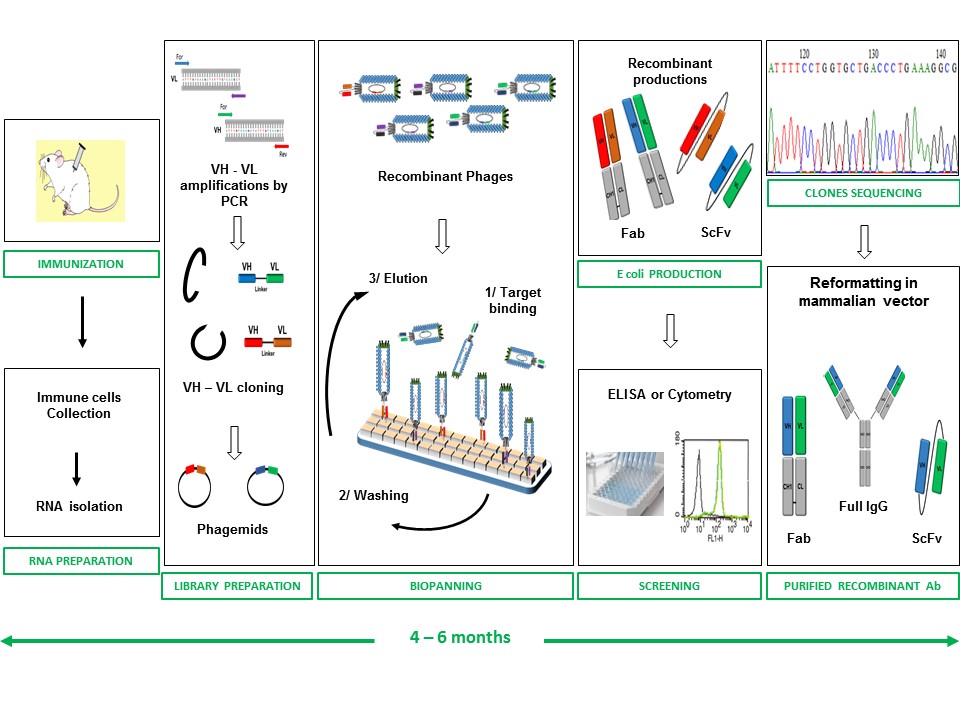
Diaclone provides purified recombinant antibodies (Fab, ScFv, Full Ig) and phage banks
Contact us for more information and a quotation
A case study:
Diaclone, with over 30 years of experience and expertise in immunology products, offers a vast catalogue of mAbs and ELISA kits for use in research and diagnostic applications. A large number of Diaclone’s products are cytokine related and specifically Interleukins (IL).
The development of the anti-IL-8 antibody was initiated in 1991, according to Köhler and Milstein’s technique (Nature-1975, 256, p495-7); six fusions were carried out giving only one specific anti-IL-8 mAb, the clone B-K8, which is still used in Diaclone’s IL-8 ELISA kit paired with a rabbit polyclonal. The aim of this project was to replace the polyclonal.
At the beginning of 2019, a new project of anti-IL-8 mAb development was initiated with a new IL-8 mouse immunization. One part of the cells from the immunized animals was unsuccessfully fused using the classical mAb method and the second was processed by the Diaclone Phage Display Platform. The phage display method (Smith, Science-1985, vol. 228, n°4705, p1315-17) is an alternative way of developing mAbs using molecular biology. The platform is capable of obtaining a strong Fab library of IgG sequences from spleen cells coming from immunized mice.
The library obtained was screened in biopanning steps with IL-8 to select very specific clones. One hundred selected Fabs were tested in ELISA to keep the best candidates. Ten of them were selected and evaluated in pairs with B-K8. Finally, we obtained four good substitutes to the polyclonal anti-IL-8. These four Fabs were sequenced and reformatted by molecular biology in full IgG to be further validated in the IL-8 Elisa kit. As a result of this project, phage display technology has demonstrated its interest, notably in allowing mAb development which was particularly difficult to obtain with a classical fusion.
Case Study Poster available here